Viral N-Glycoproteomics Service
Relying on a high-resolution LC-MS/MS platform and highly selective glycopeptide enrichment strategies, MtoZ Biolabs has developed the viral N-glycoproteomics service which enables systematic analysis of N-glycosylation modifications in viral proteins. This service covers glycopeptide enrichment, N-glycosylation site identification, glycan structure characterization, and relative quantification, allowing accurate identification of modification sites, glycan types, and distribution patterns in viral glycoproteins. With high-confidence mass spectrometry data and a professional data processing workflow, researchers can obtain comprehensive data support regarding viral glycoprotein structure, modification characteristics, and sample differences.
Overview
Viral N-glycoproteomics is the scientific field dedicated to studying N-linked glycosylation modifications in viral proteins. N-glycosylation is a common and highly conserved post-translational modification that typically occurs on asparagine (Asn) residues and plays essential roles in protein folding, stability, immune recognition, and receptor binding. Comprehensive analysis through viral N-glycoproteomics provides valuable data support for viral glycoprotein characterization, host interaction studies, and biological sample quality assessment.
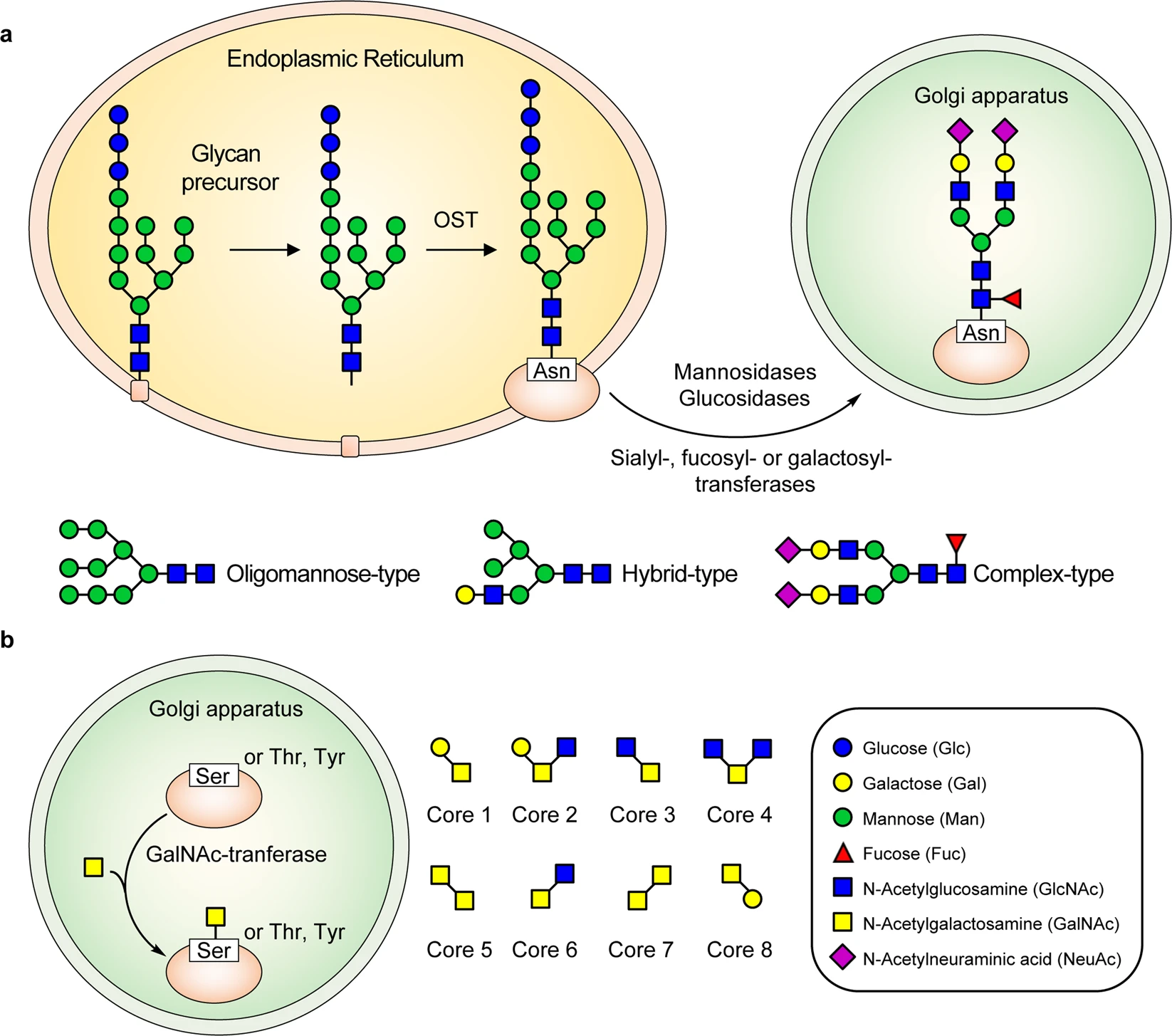
Gong, Y Q. et al. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2021.
Figure 1. The Formation Process of N-Glycosylation and O-Glycosylation in SARS-CoV-2
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation and Protein Extraction
Total proteins are extracted from viral or infected samples and enzymatically digested to obtain peptide mixtures.
2. N-Glycopeptide Enrichment
Lectin affinity, HILIC, or enzymatic deglycosylation strategies are employed to enrich N-glycosylated peptides, improving detection sensitivity.
3. Mass Spectrometry Detection and Data Acquisition
The enriched glycopeptides are analyzed using a high-resolution LC-MS/MS platform to obtain high-quality fragmentation spectra.
4. Data Analysis and Structural Identification
Database matching and algorithmic analysis are used to determine glycosylation sites, glycan compositions, and linkage types.
5. Result Integration and Report Generation
Glycosylation features are statistically analyzed and visualized, producing a complete report containing quantitative data and structural annotations.
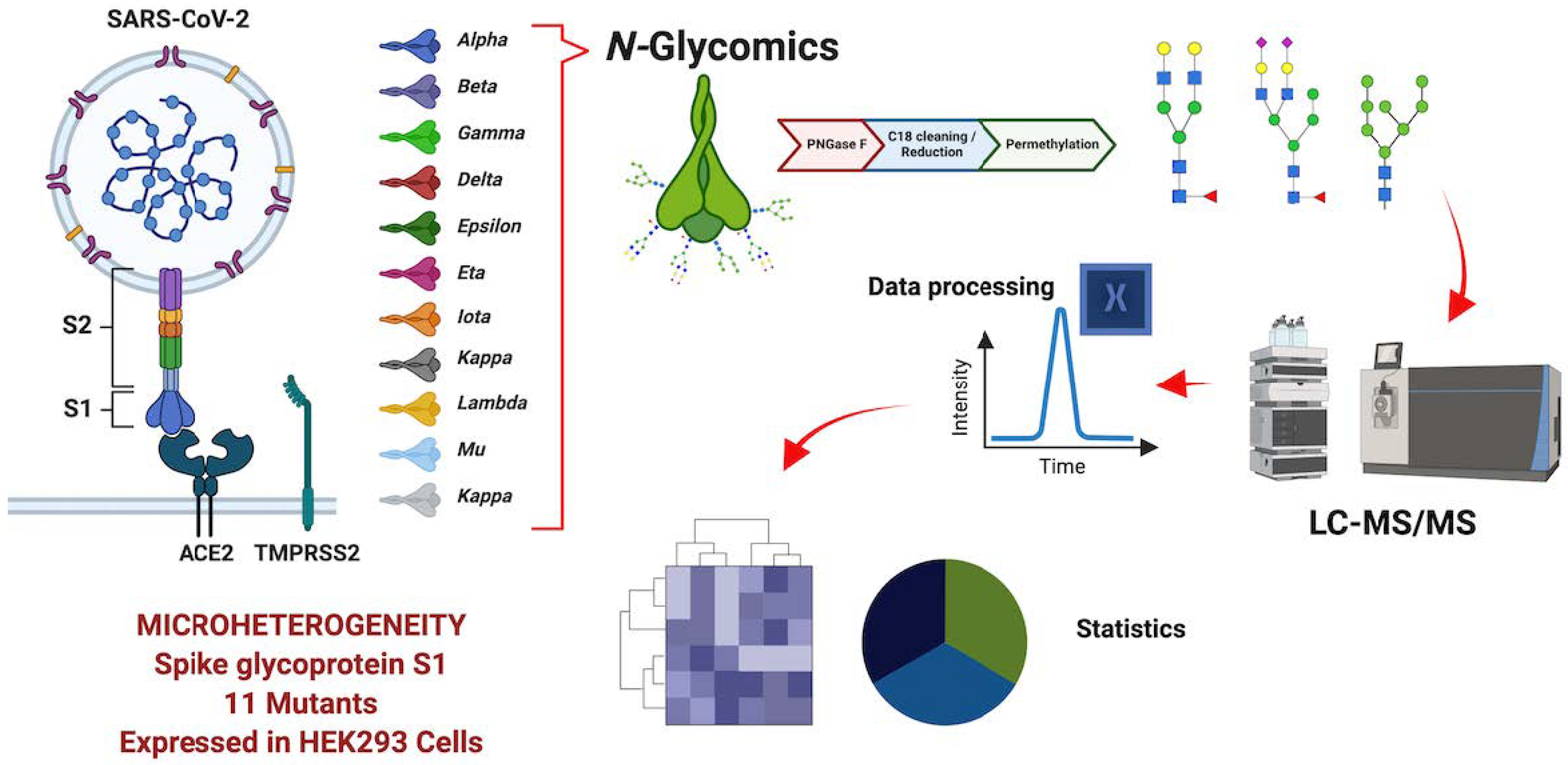
Gutierrez Reyes, C D. et al. Biomolecules, 2023.
Figure 2. The S1 Protein Derived from Eleven SARS-CoV-2 Variants Was Subjected to N-Glycomics Analysis.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
Purified viral samples, infected cell lysates, or viral protein extracts are acceptable. Freeze-dried powders, solutions, or tissue samples are also supported, making the service applicable to various viral sources.
2. Sample Storage
Samples should be stored sealed and protected from light at -80°C for long-term preservation or at -20°C for short-term use. Repeated freeze-thaw cycles should be avoided to prevent protein degradation and glycan loss.
3. Sample Transportation
Samples should be shipped in sealed, moisture-proof packaging. Liquid samples require cold-chain transportation, while freeze-dried samples may be sent at ambient temperature for short periods but must be protected from heat, humidity, and direct light.
Service Advantages
1. High-Resolution Detection Platform
Utilizing the Orbitrap LC-MS/MS system, achieving highly sensitive detection and precise quantification of N-glycopeptides.
2. Multi-Strategy Glycopeptide Enrichment
Integrating multiple enrichment approaches, such as lectin affinity, HILIC, and enzymatic deglycosylation, to enhance glycopeptide coverage and identification accuracy.
3. Experienced Technical Support
A skilled scientific team with extensive experience in glycoproteomics provides professional guidance for data interpretation and result analysis.
4. Customized Research Solutions
Analytical strategies can be flexibly tailored according to virus type and research objectives to meet diverse scientific requirements.
Applications
1. Vaccine Antigen Characterization
The viral N-glycoproteomics service can be used to analyze the N-glycosylation patterns of vaccine candidate proteins, ensuring structural stability and batch consistency.
2. Viral Evolution and Mutation Analysis
By comparing N-glycosylation differences among viral subtypes or mutant strains, researchers can explore the role of glycosylation in viral evolution.
3. Infection-Related Biomarker Discovery
The viral N-glycoproteomics service enables the identification of potential biomarkers associated with viral infection status or disease progression.
4. Integrated Multi-Omics Research
Combining proteomics, metabolomics, and glycomics data to systematically elucidate the multidimensional regulatory networks of viral infection.
FAQ
Q1: Can Glycan Structures and Modification Sites Be Analyzed Simultaneously?
A1: Yes. Through mass spectrometry analysis at the glycopeptide level combined with peptide mapping after deglycosylation, both the structural composition of glycans and the precise localization of N-glycosylation sites can be determined.
Q2: Do Different Host Cell Origins Affect the Analysis Results?
A2: Yes. Variations in glycosyltransferase systems across different hosts may lead to structural differences in glycans. Therefore, clients are advised to provide detailed information on the sample origin to ensure accurate data interpretation.
Q3: Which Viruses Are Suitable for N-Glycosylation Studies?
A3: This service is applicable to various enveloped and secreted glycoprotein viruses, including coronaviruses, influenza viruses, dengue viruses, Ebola viruses, and herpesviruses.