tRNA Modification LC-MS Analysis Service
tRNA modification refers to various chemical modifications that occur within transfer RNA molecules, such as methylation, pseudouridylation, thiolation, and deamination. These modifications are widely distributed at different positions of tRNA and play essential roles in maintaining its structural stability, ensuring accurate codon recognition, and regulating translation efficiency. Abnormal tRNA modifications are closely associated with cellular stress responses, metabolic regulation, and protein synthesis efficiency. tRNA modification analysis has become an important tool for elucidating translational regulatory mechanisms, studying RNA functions, and optimizing synthetic biology systems, and it is widely applied in molecular biology, drug development, microbial engineering, and epitranscriptomics.
Suzuki, T. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2021.
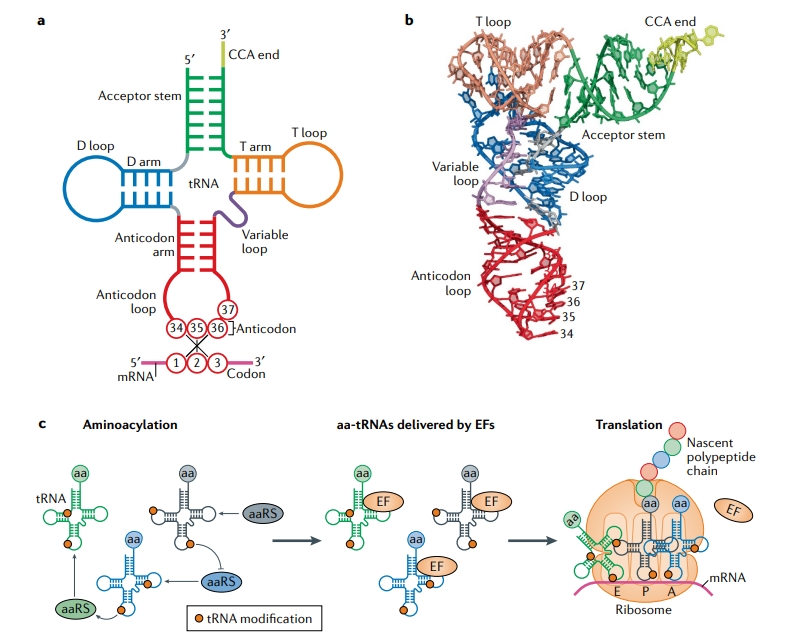
Figure 1. Basic Structure and Function of tRNA.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on a high-resolution LC-MS/MS platform, MtoZ Biolabs offers the tRNA modification LC-MS analysis service for systematic identification and quantitative analysis of chemical modifications in tRNA molecules. This service integrates enzymatic digestion, nucleoside extraction, and high-resolution mass spectrometric detection to precisely characterize the types, distribution, and abundance changes of tRNA modifications. Through standard compound comparison and database searching, high-confidence modification profiling data can be obtained, providing strong data support for researchers to uncover translational regulatory mechanisms, RNA modification networks, and cellular function regulation.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation and tRNA Extraction
Total RNA is extracted from the sample, followed by specific purification steps to obtain high-purity tRNA.
2. Enzymatic Digestion and Nucleoside Generation
The purified tRNA is enzymatically digested into individual nucleosides.
3. LC-MS/MS Detection
A high-resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) platform is used for high-sensitivity detection and separation of nucleoside samples.
4. Data Analysis and Modification Identification
Using standard calibration and database comparison, modification types and positions are identified and quantitatively analyzed.
5. Results Integration and Report Output
Modification profiling data are summarized to generate a standardized analysis report that includes modification distribution, abundance variations, and visual representations.
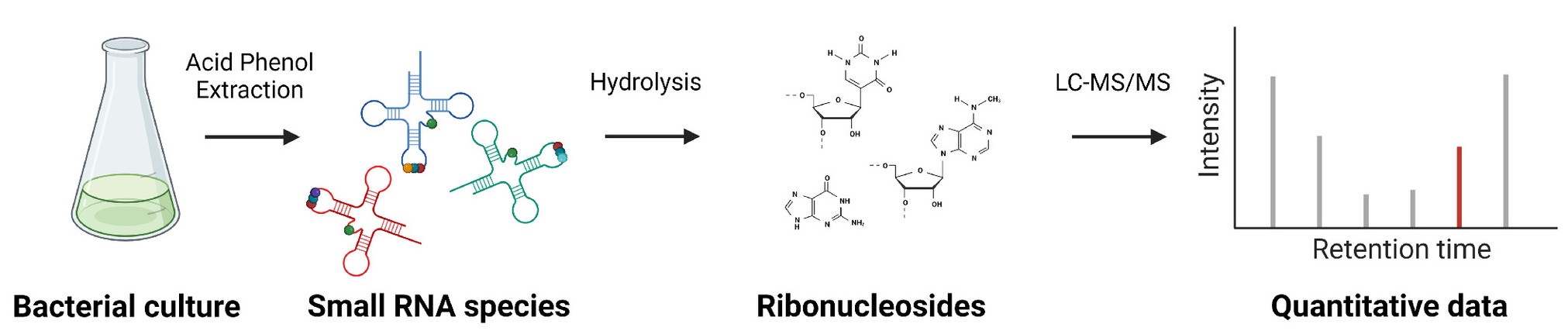
Krueger, J. et al. Biophysics and Computational Biology, 2024.
Figure 2. Targeted LC-MS/MS based Quantification of Modified tRNA Uridine Derivatives.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
Cell, tissue, blood, and microbial samples are accepted, as well as total RNA or purified tRNA forms.
Note: Samples should be free from degradation and contamination to ensure analytical accuracy.
2. Sample Storage
RNA samples should be sealed and stored in an RNase-free environment. For long-term preservation, store at -80°C; for short-term storage, -20°C is acceptable. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles and exposure to high temperatures.
3. Sample Transportation
Liquid samples are recommended to be transported on dry ice. Lyophilized samples may be shipped at room temperature for short periods but should be protected from light, moisture, and heat to maintain modification stability and sample integrity.
Service Advantages
1. High-Resolution Detection Capability
Utilizing an advanced LC-MS/MS platform, this service enables highly sensitive detection and precise quantification of tRNA modifications.
2. Comprehensive Modification Coverage
Capable of identifying multiple types of tRNA chemical modifications simultaneously, revealing their distribution characteristics and variation patterns.
3. Standardized Analytical Workflow
Every step from RNA extraction to data interpretation follows strict quality control to ensure accuracy and reproducibility.
4. Customized Research Solutions
Analytical strategies are flexibly designed according to research goals, supporting diverse experimental needs.
Applications
1. Translational Regulation Studies
tRNA modification LC-MS analysis service can be used to evaluate the roles of different modifications in regulating translation efficiency and fidelity.
2. Development and Differentiation Research
By monitoring tRNA modification dynamics during developmental stages or cell differentiation, this service helps explore their functions in gene expression regulation.
3. RNA Stability Studies
By analyzing how modifications affect tRNA structure and stability, it assesses their role in maintaining RNA functionality.
4. Metabolism and Energy Balance Research
tRNA modification LC-MS analysis service reflects cellular metabolic states, providing insights into the regulation of energy metabolism and nutrient-sensing pathways.
FAQ
Q1: Does Sample Purity Affect the Analytical Results?
A1: Yes. The purity of tRNA samples significantly impacts detection sensitivity and quantitative accuracy. It is recommended to use highly purified tRNA samples with rRNA and mRNA thoroughly removed to obtain high-quality data.
Q2: Can Modification Levels Be Quantitatively Compared between Different Samples?
A2: Yes. By applying TMT, SILAC, or Label-Free strategies, tRNA modification levels under different experimental conditions can be quantitatively compared and analyzed.
Q3: Can LC-MS/MS Detect Low-Abundance Modifications?
A3: Yes. By optimizing enrichment, separation, and ionization conditions, LC-MS/MS enables highly sensitive detection of low-abundance or rare modified nucleosides.