Protein PEGylation Analysis Service
Relying on advanced analytical platforms such as high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), liquid chromatography (LC), and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), MtoZ Biolabs has launched the protein PEGylation analysis service which can comprehensively analyze the site specificity, structural integrity, and molecular heterogeneity of protein PEGylation, and evaluate the distribution characteristics and variations of PEGylation modifications in protein molecules. The final output data include precise identification of PEGylation sites, quantitative information, structural stability, and modification heterogeneity, providing reliable support for researchers to conduct in-depth studies on protein function and biopharmaceutical quality assessment.
Overview
Protein PEGylation refers to the process in which polyethylene glycol (PEG) molecules are covalently attached to specific sites of proteins through chemical or enzymatic reactions. This modification can significantly improve protein solubility, stability, and in vivo circulation half-life, while reducing immunogenicity and protease degradation rate. Protein PEGylation analysis has been widely applied in biopharmaceutical quality control, protein drug development, structural and functional studies, and novel biomaterial development, providing reliable data support for optimizing protein molecular performance and expanding application prospects.
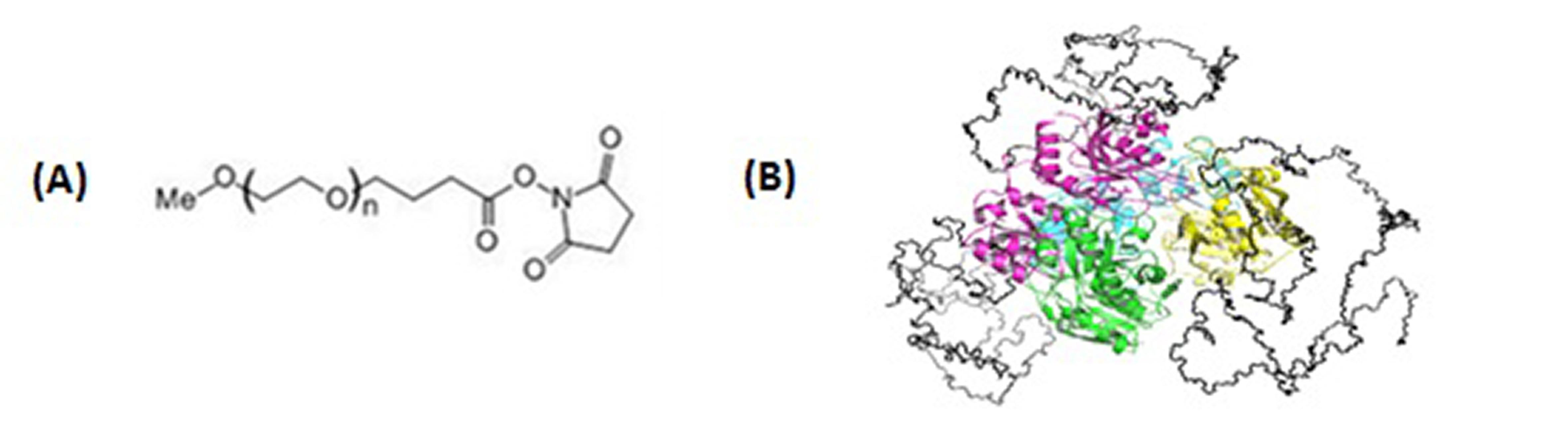
Santos, J H P M. et al. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2018.
Figure 1. Chemical Structure of N-Terminal Reactive PEG and Schematic Representation of Its Tetrameric Protein.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
1. Target Protein PEGylation Analysis
MtoZ Biolabs can perform precise detection of PEGylation modifications on specific target proteins, identifying the attachment sites, types, and modification levels of PEG. Using high-resolution LC-MS/MS, we can evaluate the effects of PEGylation on protein structure, stability, and function, providing reliable evidence for modification optimization in drug development.
2. PEGylated Proteomics Analysis
By integrating enrichment methods with high-throughput mass spectrometry platforms, MtoZ Biolabs can systematically identify and quantify PEGylated peptides in complex systems, generating a global PEGylation modification profile. This analysis can reveal PEGylation distribution trends under different conditions and support mechanism studies, quality control, and biopharmaceutical development.
Analytical Methods
The protein PEGylation detection methods provided by MtoZ Biolabs include but are not limited to the following:
1. LC-MS/MS
High-resolution liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry is used to perform precise qualitative and quantitative analysis of PEGylated proteins, directly identifying modification sites and abundance changes.
2. Chromatography
(1) Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
Separates PEGylated and unmodified proteins based on molecular size to evaluate the impact of modifications on molecular homogeneity and aggregation.
(2) Reverse Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
Separates modified proteins or peptides according to hydrophobicity differences, detecting PEGylation degree and purity characteristics.
3. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR) (if applicable)
Analyzes spatial conformation and structural integrity of PEGylation modifications through chemical shifts and peak shape changes, providing structural information at the molecular level.
4. Western Blot/ELISA
Uses specific antibodies to detect the presence and expression level of PEGylated proteins, which can be applied for modification validation and semi-quantitative analysis.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types
We can accept various types of samples such as cells, tissues, body fluids, and purified proteins.The samples must contain sufficient protein amounts to ensure the reliability of PEGylation modification detection and quantitative analysis.
2. Sample Storage
It is recommended that samples be stored at -80°C for long-term preservation, avoiding repeated freeze-thaw cycles to minimize protein degradation and loss of modifications.
3. Sample Transportation
Samples should be transported on dry ice or under cold chain conditions and protected with sealed containers to ensure sample integrity and modification stability during transportation.
Service Advantages
1. Comprehensive Coverage
Systematically detects site specificity, structural integrity, and molecular heterogeneity of protein PEGylation, ensuring results are comprehensive and reliable.
2. High Sensitivity and High Resolution
Utilizes advanced platforms such as LC-MS/MS and NMR to accurately capture low-abundance modifications in complex samples, ensuring data precision and credibility.
3. Multi-Technology Integration
Combines mass spectrometry, chromatography, and immunological methods to validate PEGylation modifications from different perspectives, enhancing the accuracy and reliability of detection results.
4. One-Stop Support
Provides complete solutions from sample preparation and modification detection to data analysis, helping researchers efficiently obtain systematic PEGylation analysis data.
Applications
1. Protein Stability Evaluation
By detecting PEGylation modification levels, the stability and degradation trends of proteins under different conditions can be studied to support long-term protein research.
2. Modification Heterogeneity Characterization
Protein PEGylation analysis service can be used to analyze the distribution and differences of PEGylation modification sites, helping researchers comprehensively understand protein PEGylation features.
3. Biopharmaceutical Quality Control
In the detection of antibodies, recombinant proteins, and other biopharmaceuticals, the degree and consistency of PEGylation modifications are key indicators for evaluating product quality and reliability.
4. Functional Validation
Protein PEGylation analysis service can help confirm the effects of modifications on protein activity, interactions, and functional performance, providing data support for subsequent research.
FAQ
Q1: Is It Necessary to Enrich PEGylated Proteins?
A1: Not all samples require enrichment. For samples with a high proportion of PEGylation, direct mass spectrometry detection can be performed; for samples with low modification content, it is recommended to combine affinity chromatography or specific chemical labeling to improve the signal-to-noise ratio and detection sensitivity.
Q2: Can PEGylation Modifications Be Quantitatively Analyzed?
A2: Yes. Common strategies include label-free quantification, isotope labeling (such as TMT, iTRAQ), and DIA methods. Appropriate quantification approaches can be selected based on research needs.
Q3: What Are the Limitations of PEGylation Modification Detection?
A3: For very low-abundance or highly heterogeneous PEG modifications, detection sensitivity may be limited. In addition, PEGylation may reduce chromatographic separation efficiency, requiring optimization of separation methods and mass spectrometry parameters to improve detection performance.