Quantitative Glycoproteomics Analysis Service
At MtoZ Biolabs, our Quantitative Glycoproteomics Analysis Service integrates advanced glycopeptide enrichment strategies, high-resolution LC-MS/MS platforms, and flexible quantification workflows to deliver precise and reproducible results. We offer both labeling-based approaches, including TMT, iTRAQ, SILAC, and dimethyl labeling, as well as label-free DIA and DDA strategies to accommodate diverse research and industrial needs. By combining robust bioinformatics pipelines with curated glycan databases, we provide clients with reliable quantitative data and functional insights that support therapeutic protein characterization, disease biomarker discovery, and regulatory-compliant biopharmaceutical development.
Overview
Quantitative glycoproteomics is a specialized field of proteomics dedicated to the large-scale measurement of glycosylated proteins and glycopeptides with site-specific resolution. Unlike qualitative glycoproteomics, which focuses on identifying glycosylation sites and glycan structures, quantitative glycoproteomics provides dynamic information on glycosylation occupancy, glycoform distribution, and abundance changes under different biological conditions. This is particularly critical because protein glycosylation exhibits both macro-heterogeneity, defined by the presence or absence of glycans at specific sites, and micro-heterogeneity, which reflects the diversity of glycan structures attached to a given site.
With the development of high-resolution mass spectrometry and advanced labeling and label-free strategies, quantitative glycoproteomics has become an indispensable tool for investigating disease-associated glycosylation changes, discovering biomarkers, and ensuring the quality and consistency of therapeutic proteins. By enabling precise and reproducible quantification, this approach bridges fundamental biology and translational research, offering insights into molecular mechanisms and supporting regulatory-compliant biopharmaceutical development.
Technical Principles
Quantitative glycoproteomics analysis is based on high-resolution mass spectrometry coupled with specific quantification strategies to measure glycopeptide abundance at the proteome scale. The principle relies on detecting intact glycopeptides and their fragment ions, which simultaneously provide information on the peptide backbone and attached glycans. Quantification can be achieved through two main strategies: labeling-based methods, which incorporate stable isotopes into peptides or glycans for multiplexed and accurate relative quantification, and label-free methods, which measure MS signal intensities directly, often using data-independent acquisition (DIA) or data-dependent acquisition (DDA). By integrating these acquisition strategies with robust computational algorithms and curated glycan databases, the approach enables precise quantification of site-specific glycosylation occupancy and glycoform heterogeneity across complex biological samples.
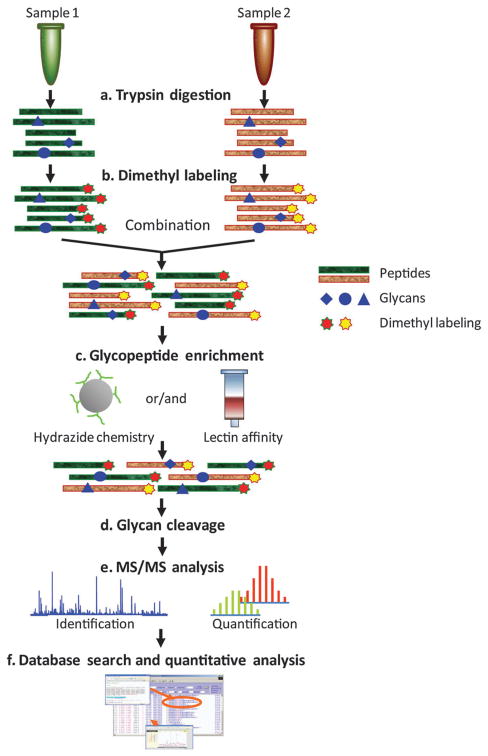
Pan S. et al. Mol Biosyst. 2012.
Figure 1. Analytical flow for global quantitative profiling of site-specific glycosylation occupancy
Analysis Workflow
The general analytical workflow for the Quantitative Glycoproteomics Analysis Service is as follows:
1. Sample Preparation and Protein Extraction
Proteins are isolated from biological or pharmaceutical samples under optimized conditions, followed by digestion with proteases such as trypsin to generate glycopeptides.
2. Glycopeptide Enrichment
Specialized enrichment methods, including HILIC, lectin affinity, hydrazide chemistry, or other strategies, are applied to increase the detection sensitivity of glycopeptides.
3. Quantification Strategy Implementation
Depending on study objectives, samples undergo isotope-based labeling methods (TMT, iTRAQ, SILAC, or dimethyl labeling) or are processed using label-free workflows such as DIA or DDA.
4. LC-MS/MS Data Acquisition
High-resolution LC-MS/MS is performed to detect both peptide backbones and glycan-derived fragment ions, ensuring comprehensive coverage of glycoproteomes.
5. Data Processing and Quantitative Analysis
Advanced bioinformatics pipelines deconvolute spectra to identify glycosylation sites, annotate glycan structures, and quantify site occupancy and glycoform distributions.
6. Biological Interpretation and Reporting
Results are integrated with functional annotation tools such as GO and KEGG, and presented in detailed reports including glycosylation maps, quantitative profiles, and structural insights.
Service Advantages
1. Advanced Analysis Platform
MtoZ Biolabs established an advanced Quantitative Glycoproteomics Analysis Service platform, guaranteeing reliable, fast, and highly accurate analysis service.
2. Comprehensive Quantification
Accurate measurement of both N- and O-linked glycopeptides, including site occupancy and glycoform heterogeneity, ensuring full-spectrum glycoproteome coverage.
3. Flexible Quantification Strategies
Support for multiple workflows such as TMT, iTRAQ, SILAC, dimethyl labeling, and label-free DIA/DDA methods, tailored to the specific needs of discovery or targeted studies.
4. Advanced Bioinformatics Integration
Robust pipelines with curated glycan databases deliver accurate site-specific assignment, structural annotation, and functional interpretation.
Sample Submission Suggestions
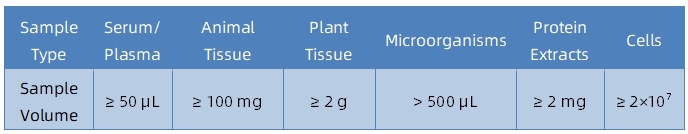
It is recommended to contact our technical support team before submitting samples to determine sample suitability and obtain tailored submission guidelines.
Applications
Applications of the Quantitative Glycoproteomics Analysis Service include but are not limited to:
1. Glycosylation Dynamics in Developmental Biology
Quantitative profiling of glycosylation during embryonic development or tissue differentiation to understand stage-specific regulatory mechanisms.
2. Neurological Disorders Research
Investigation of glycosylation changes in synaptic proteins and ion channels, revealing potential roles in disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease or Parkinson’s disease.
3. Immunotherapy Optimization
Characterization of glycosylation on immune checkpoint proteins or engineered antibodies to improve therapeutic efficacy and reduce immunogenicity.
4. Metabolic Disease Studies
Linking glycoproteomic alterations to metabolic pathways, providing insights into diseases such as diabetes, obesity, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.