Histone PTM Site Identification Service
Based on the high-resolution LC-MS/MS platform, MtoZ Biolabs' histone PTM site identification service enables precise identification and characterization of various post-translational modifications (PTMs) on histones. Through optimized sample preparation and spectral interpretation workflows, it accurately determines the modified amino acid residues and their modification types. Combined with bioinformatics analysis, the service provides detailed outputs such as modification site lists, sequence localization, and distribution patterns, offering reliable data support for studying histone modification profiles and epigenetic regulatory mechanisms.
Overview
Histone post-translational modifications (PTMs) refer to diverse chemical modifications occurring on histones after translation, including acetylation, methylation, and phosphorylation, which serve as key mechanisms for regulating chromatin structure and gene transcription activity. Different modification sites determine specific regulatory roles; therefore, accurate identification of modified amino acid residues is essential for elucidating epigenetic control mechanisms. Histone PTM site identification reveals modification distribution patterns and specific regulatory features, providing fundamental data for studying gene expression regulation, signaling pathway modulation, and modification interaction networks, and it is widely applied in epigenetics, developmental biology, and cellular function research.
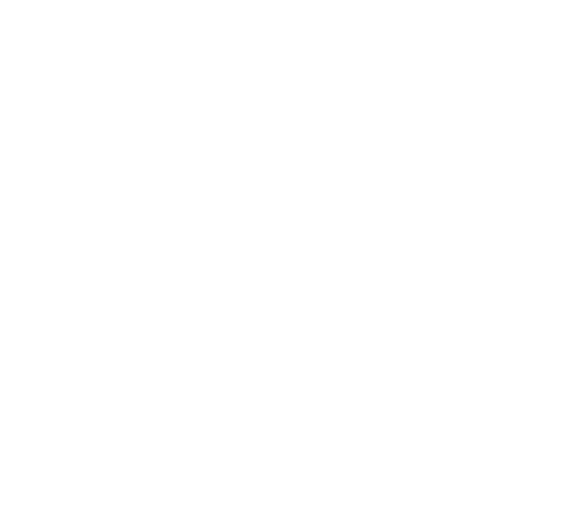
Liu, R Q. et al. MedComm, 2023.
Figure 1. Post-Translational Modifications (PTMs) of Histone Amino Terminus.
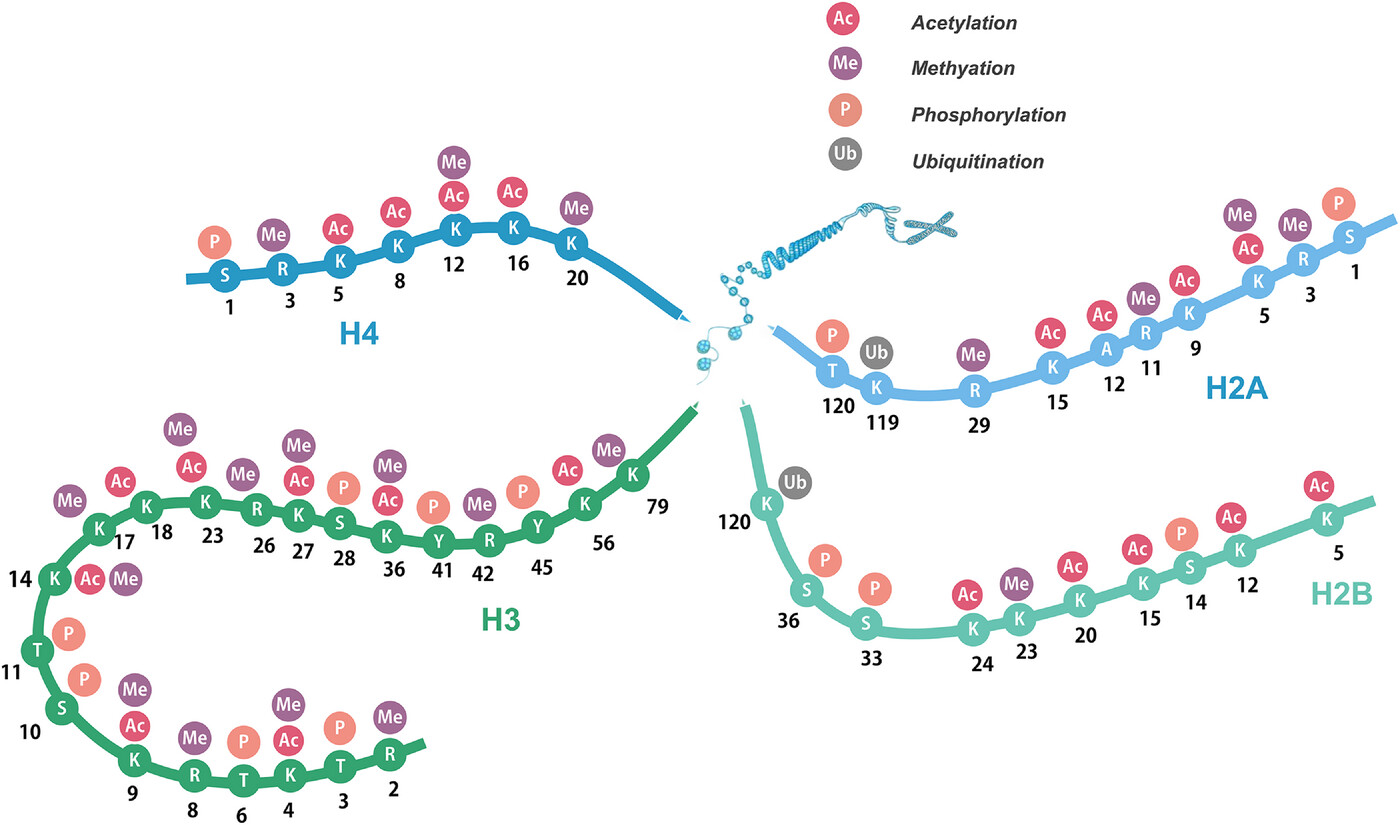
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation
Histones are extracted from samples and digested under mild conditions to generate detectable peptides.
2. Modified Peptide Enrichment
Specific enrichment strategies are applied to selectively capture target modified peptides.
3. Mass Spectrometry Detection
Using a high-resolution LC-MS/MS platform, modified peptides are precisely identified, and modification sites are determined.
4. Spectral Interpretation and Site Localization
High-confidence spectral matching and algorithmic analysis are used to accurately localize modification types and amino acid residues.
5. Data Processing and Result Output
A comprehensive modification site list and localization confidence report are generated to support subsequent functional studies.
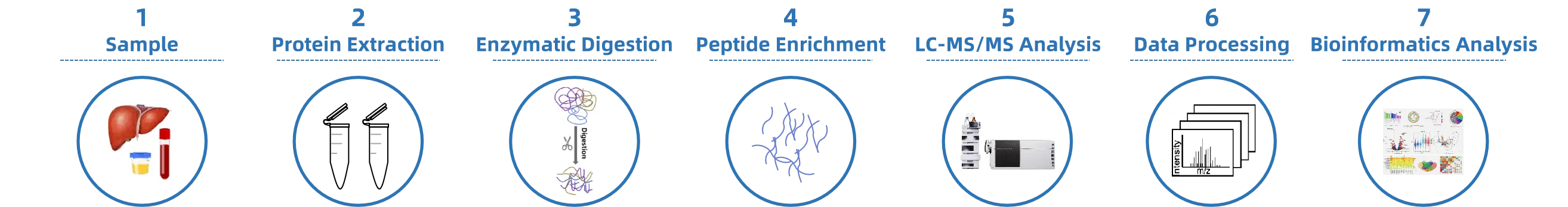
Figure 2. The Workflow of Histone PTM Site Identification.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type and Quantity
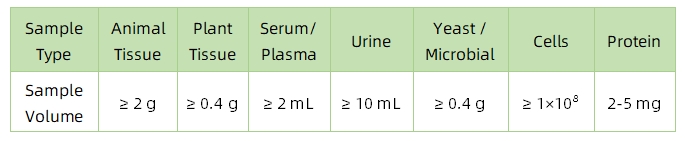
Note: Plasma should be collected using EDTA as an anticoagulant. Standard tissue or cell lysis buffers can be used during protein extraction.
2. Sample Transportation
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Samples are recommended to be stored at -80°C and transported on dry ice to ensure low-temperature conditions throughout the process and prevent modification loss.
Note: For special samples or if a detailed submission plan is required, please contact MtoZ Biolabs technical staff in advance.
Service Advantages
1. High-Resolution Site Analysis
Combining a high-resolution LC-MS/MS platform with advanced algorithmic models, this approach achieves precise localization and confidence assessment of histone modification sites.
2. Comprehensive PTM Coverage
Simultaneous identification of multiple PTM types, including acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, and ubiquitination, enables a complete histone modification profile.
3. Flexible Analytical Customization
Experimental strategies are tailored based on research objectives, sample characteristics, and modification types to meet diverse and specific study requirements.
4. Professional Data Reporting
Structured modification site lists and functional annotation results are provided to facilitate further mechanistic exploration.
Applications
1. Epigenetic Regulation Research
The histone PTM site identification service can be used to analyze the role of histone modification sites in chromatin structure modulation and gene expression regulation.
2. Development and Differentiation Studies
By comparing modification site differences among various tissues or cell types, this service helps reveal their functional roles during developmental processes.
3. Signal Transduction and Cellular Response
The histone PTM site identification service enables exploration of dynamic changes in modification sites following environmental stimuli or pathway activation.
4. Functional Biomarker Discovery
Through analysis of modification site distribution and abundance variations, this service supports the identification of potential epigenetic biomarkers.
FAQ
Q1: How Is the Accuracy of Site Identification Ensured?
A1: This service relies on high-resolution LC-MS/MS combined with multi-stage fragmentation (MSⁿ) and precise database-matching algorithms. Modification site localization is determined based on exact mass differences and ion fragmentation patterns, ensuring accurate single-residue identification and validation.
Q2: How Are Ambiguities Caused by Isomeric or Adjacent Modification Sites Resolved?
A2: Sequence coverage is enhanced using EThcD/ECD fragmentation modes, complemented by manual verification and site probability modeling, to distinguish adjacent modification sites and multiple modification isomers.
Q3: Does the Service Support Multi-sample or Group Comparison?
A3: Yes. It allows for comparative analysis of site distribution and abundance across different experimental conditions or time points, revealing dynamic regulatory characteristics.