Protein Deamidation Analysis Service
Based on high-resolution LC-MS/MS mass spectrometry and high-performance liquid chromatography platforms, the protein deamidation analysis service launched by MtoZ Biolabs enables systematic analysis of deamidation modification sites in protein samples. This service, through optimized sample processing and specific data analysis methods, achieves precise identification and quantification of deamidation sites, providing information including site distribution, modification levels, and abundance changes. The final data not only help researchers evaluate protein structural stability and functional changes but can also be used for quality control, structural research, and functional exploration, providing reliable data support for scientific research and industrial applications.
Overview
Protein deamidation refers to the process in which asparagine (Asn) or glutamine (Gln) residues in proteins are converted into aspartic acid (Asp), isoaspartic acid (isoAsp), or glutamic acid (Glu) through spontaneous chemical reactions or enzymatic action, which is a common and slowly accumulating post-translational modification. This modification may alter the charge state, structural stability, and biological function of proteins, thereby affecting molecular activity and lifespan. Its analysis mainly relies on high-resolution liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) technology, combined with specific data analysis methods, to achieve precise identification and quantification of deamidation sites. This service is widely applied in protein drug stability and quality control, food and nutritional protein research, as well as aging-related protein function analysis, providing reliable data support for basic scientific research and industrial applications.
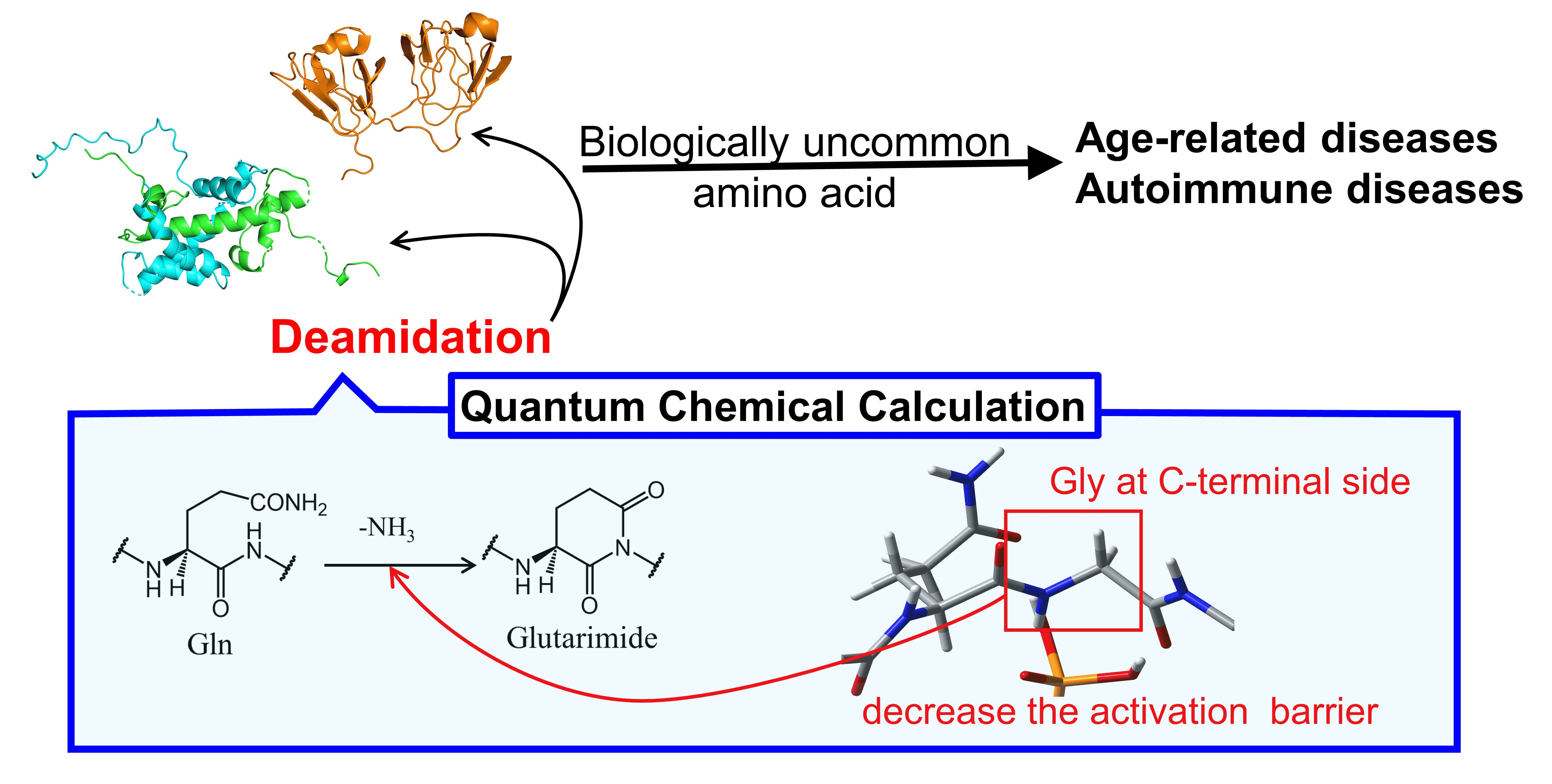
Asai, H. K. et al. AppliedChem. 2021.
Figure 1. Protein Deamidation Modification Process.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
1. Target Protein Deamidation Analysis
MtoZ Biolabs can perform site-level deamidation detection for specific target proteins, identifying the deamidation positions and changes of asparagine and glutamine residues. Relying on high-resolution LC-MS/MS, we can quantify modification trends under different conditions and provide key data for protein stability and functional analysis.
2. Deamidation Proteomics Analysis
MtoZ Biolabs combines efficient separation with large-scale mass spectrometry detection to systematically identify and quantify deamidated peptides in complex samples. This service can reveal global deamidation patterns, supporting regulatory network studies, sensitive site screening, and the exploration of protein aging and stress response mechanisms.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation
Perform protein extraction and quantification from samples such as cells, tissues, or body fluids to ensure quality and uniformity.
2. Protein Digestion
Use trypsin or other enzymes to digest proteins into peptides, facilitating the subsequent detection of deamidation sites.
3. Modification Detection
Conduct high-sensitivity detection of potential deamidated peptides through a high-resolution LC-MS/MS platform combined with liquid-phase separation technology.
4. Data Analysis
Apply specific data processing algorithms to accurately identify and quantify deamidation sites, providing information on modification distribution, abundance changes, and related functional characteristics.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types
A wide range of biological samples is accepted, including cells, tissues, body fluids, and purified proteins, ensuring sufficient protein content to support deamidation detection and quantitative analysis.
2. Sample Storage
It is recommended to store samples at -80°C and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles to prevent protein degradation and loss of modifications.
3. Sample Transportation
Samples should be transported on dry ice or under cold-chain conditions, using sealed containers to ensure stability and integrity during delivery to the testing platform.
Service Advantages
1. High-Sensitivity Detection
Relying on a high-resolution LC-MS/MS platform, low-abundance deamidation modifications can be captured even in complex backgrounds, ensuring accuracy and reliability of detection.
2. Specific Data Analysis
By combining optimized algorithms and databases, precise identification and quantification of deamidation sites can be achieved, delivering high-confidence results.
3. Expert Team Support
Experiments and data analysis are carried out by experts with extensive experience in proteomics and post-translational modification studies, ensuring standardized procedures and trustworthy results.
4. Flexible Customized Solutions
The analysis depth and scope can be adjusted according to research objectives, providing targeted solutions to meet diverse scientific or industrial application needs.
Applications
1. Protein Stability Research
Protein deamidation analysis service can be used to evaluate protein structural stability and degradation trends under different conditions.
2. Aging and Protein Modification Research
As a common age-related modification, deamidation can be used to explore structural and functional changes in proteins during aging.
3. Food and Nutrition Analysis
Protein deamidation analysis service can be applied to study structural changes in proteins during food processing or storage, revealing their impact on nutritional properties and functionality.
4. Structural Biology and Functional Analysis
By analyzing the distribution and abundance of deamidation modifications, insights can be gained into protein conformation, molecular interactions, and functional characteristics.
FAQ
Q1: Does Protein Deamidation Easily Occur during Sample Storage?
A1: Yes. Deamidation can occur spontaneously under certain temperature and pH conditions. Therefore, samples should be stored at -80°C and repeated freeze-thaw cycles should be avoided to minimize artificial modifications.
Q2: Can Deamidation Modifications Be Quantitatively Analyzed?
A2: Yes. Label-free quantification, isotope labeling (TMT/iTRAQ), and DIA strategies are supported, which can be used to compare modification levels under different conditions.
Q3: Is Integration with Other Proteomics Data Supported?
A3: Yes. Deamidation data can be combined with whole-protein quantification, phosphorylation, acetylation, and other modification results to enable integrated studies of regulatory mechanisms and multidimensional comparisons.
Deliverables
In the technical report, MtoZ Biolabs will provide you with detailed technical information, including:
1. Experimental Procedures
2. Relevant Experimental Parameters
3. Detailed Information on Protein Deamidation Modifications
5. Raw Data
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.