Protein Alkylation Analysis Service
Based on advanced technology and analytical platforms, MtoZ Biolabs has launched the protein alkylation analysis service to comprehensively identify and quantify alkylation modifications in protein samples. This service combines specific enrichment and optimized experimental workflows to analyze the distribution and levels of alkylation modification sites, evaluate their dynamic changes, and characterize their functional features. The final output data include precise identification results of modification sites, quantitative difference information, and related functional annotations, providing reliable support for researchers in protein function studies, structural analysis, and cellular regulation exploration. MtoZ Biolabs provides detection methods including but not limited to the following:
1. Mass Spectrometry
Through high-resolution LC-MS/MS combined with liquid chromatography separation, this method enables accurate qualitative and quantitative analysis of alkylated peptides, allowing simultaneous identification of modification sites and abundance changes.
2. Immunoblotting
By using specific anti-alkylation antibodies to detect protein samples, followed by electrophoretic separation and membrane transfer with color development, this method directly reflects the presence and levels of modified proteins.
3. Immunofluorescence Technology
By applying fluorescently labeled antibodies combined with microscopic imaging, this method allows direct observation of the localization and distribution of alkylated proteins at the cellular or tissue level.
Overview
Protein alkylation refers to the process in which an alkyl group covalently attaches to amino acid residues of proteins (such as cysteine, lysine, or histidine) under the action of specific enzymes or chemical reagents. This modification can alter the charge state, spatial conformation, and interaction properties of proteins, thereby affecting their stability, activity, and signaling pathway functions. Protein alkylation analysis is widely applied in structural biology, cell signaling research, protein function regulation, and the exploration of environmental stress mechanisms, providing reliable data support for understanding protein modification networks and cellular regulation.
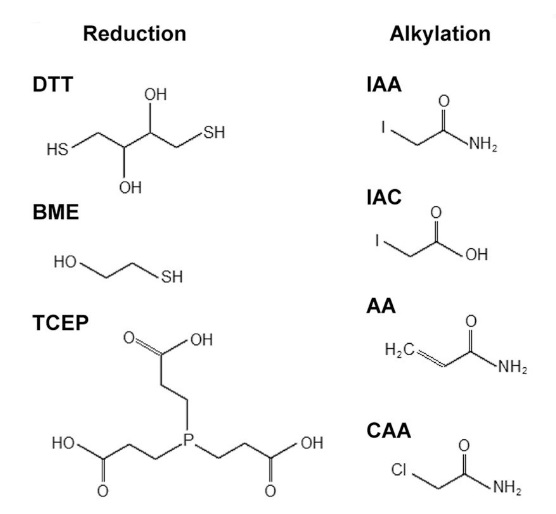
Müller, T. et al. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 2017.
Figure 1. Frequently Used Reduction and Alkylation Reagents.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
1. Target Protein Alkylation Analysis
MtoZ Biolabs can perform site-level alkylation modification detection for specific target proteins, characterizing the locations and types of alkylation as well as their variation trends under different treatment conditions. Relying on a high-resolution LC-MS/MS platform, we assist researchers in evaluating the impact of alkylation on protein activity, structural stability, and regulatory properties.
2. Alkylation Proteomics Analysis
MtoZ Biolabs combines alkylated peptide enrichment strategies with high-throughput mass spectrometry systems to systematically identify and quantify large numbers of alkylated peptides in complex samples. This analysis enables the construction of a global alkylation modification map and reveals its distribution patterns and functional characteristics in cellular homeostasis, stress responses, and metabolic regulation.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation
Extract target proteins from cells, tissues, body fluids, or purified proteins and perform quantitative measurements to ensure sample uniformity and quality.
2. Protein Digestion
(1) In-solution digestion: Proteins are first reduced to break disulfide bonds; subsequently, alkylation is performed to block free sulfhydryl groups and prevent disulfide bond reformation; finally, proteases such as trypsin are used to cleave proteins into peptides for subsequent detection.
(2) In-gel digestion: Suitable for protein bands separated by SDS-PAGE. Proteins in the gel also undergo reduction, alkylation, and enzymatic digestion, after which the resulting peptides are extracted for analysis.
3. Enrichment of Alkylated Peptides
Alkylated peptides are selectively enriched using affinity chromatography, specific antibodies, or chemical labeling methods, improving the detection rate of low-abundance modifications.
4. Mass Spectrometry Detection
High-resolution LC-MS/MS combined with liquid chromatography separation is employed to accurately identify and quantify the enriched peptides, analyzing modification types, distribution, and abundance changes.
5. Data Analysis
Database searching and bioinformatics analysis are applied to output the identification and quantification results of modification sites, along with functional annotations and potential regulatory information.
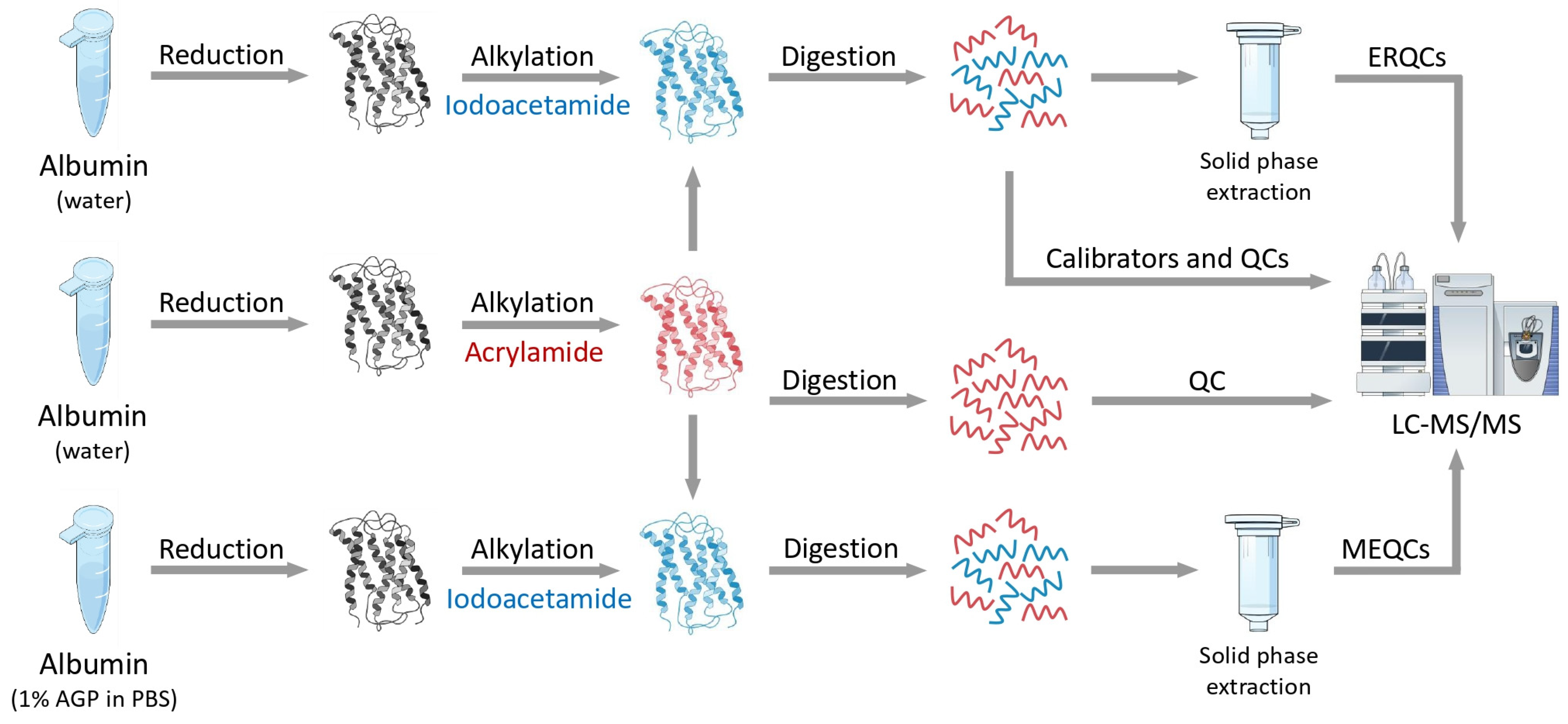
Virág, D. et al. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2024.
Figure 2. The Workflow of Protein Alkylation Analysis Based on LC-MS/MS.
Service Advantages
1. Multiple Modification Coverage
Capable of simultaneously detecting various alkylation modifications on cysteine, lysine, histidine, and other residues, ensuring comprehensive and systematic results.
2. High Sensitivity
With the support of a high-resolution LC-MS/MS platform, low-abundance alkylation modifications can be captured in complex backgrounds, ensuring data accuracy.
3. Multi-Technology Integration
By combining mass spectrometry, immunoblotting, and immunofluorescence methods, modification states can be confirmed at multiple levels, enhancing result reliability.
4. Customized Service
Analytical strategies can be flexibly adjusted according to different research objectives, providing personalized alkylation detection and functional interpretation support.
Applications
1. Modification Dynamics Study
Protein alkylation analysis service can be used to analyze the dynamic variation patterns of modifications, revealing their temporal characteristics in cellular responses.
2. Modification Interaction Analysis
Alkylation often intersects with modifications such as phosphorylation and oxidation. Combined analysis helps to understand the regulatory relationships among multiple modifications.
3. Biomarker and Chemical Probe Validation
Protein alkylation analysis service can be applied to validate its specificity, coverage, and modification efficiency.
4. Environmental and Stress Adaptation Research
Under oxidative stress or external environmental conditions, protein alkylation levels may change significantly. Analytical results help to study cellular adaptation and response mechanisms.
FAQ
Q1: Is Enrichment Necessary for Protein Alkylation Detection?
A1: In general, common reduction–alkylation modifications can be directly detected by mass spectrometry. However, if the target is low-abundance or specific types of alkylation modifications, it is recommended to combine affinity chromatography or chemical labeling for enrichment to improve sensitivity and signal-to-noise ratio.
Q2: What Are the Sample Requirements for Protein Alkylation Detection?
A2: It is recommended to provide cell, tissue, body fluid, or purified protein samples with sufficient protein content. Samples should be stored at -80°C and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Transport should be carried out on dry ice or under cold-chain conditions to ensure modification stability.
Q3: What Are the Limitations of Alkylation Analysis?
A3: Detection sensitivity may be limited for extremely low-abundance or unstable modification sites. In addition, some novel types of alkylation lack comprehensive database annotations, and result interpretation requires experimental validation and literature evidence.