Histone Crotonylation Analysis Service
Based on the high-resolution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) platform, the histone crotonylation analysis service provided by MtoZ Biolabs can perform systematic detection and quantitative analysis of crotonylation (Kcr) modifications on histone lysine residues. This service can accurately identify Kcr modifications at different sites and compare their abundance changes under different conditions. By integrating bioinformatics tools, it can output high-quality data such as modification distribution, quantitative differences, and functional annotation, providing reliable data support for researchers to further explore crotonylation.
Overview
Histone crotonylation (Kcr) is a type of post-translational modification occurring on lysine residues, in which the attachment of a crotonyl group can alter chromatin structure and influence gene transcription. As an emerging epigenetic modification, Kcr plays a unique role in transcriptional activation, chromatin remodeling, and cell fate determination, and is closely associated with epigenetic regulation. Histone crotonylation analysis can achieve precise detection and quantification of Kcr modifications and is widely applied in epigenetics research, gene transcription mechanism exploration, and potential biomarker screening.
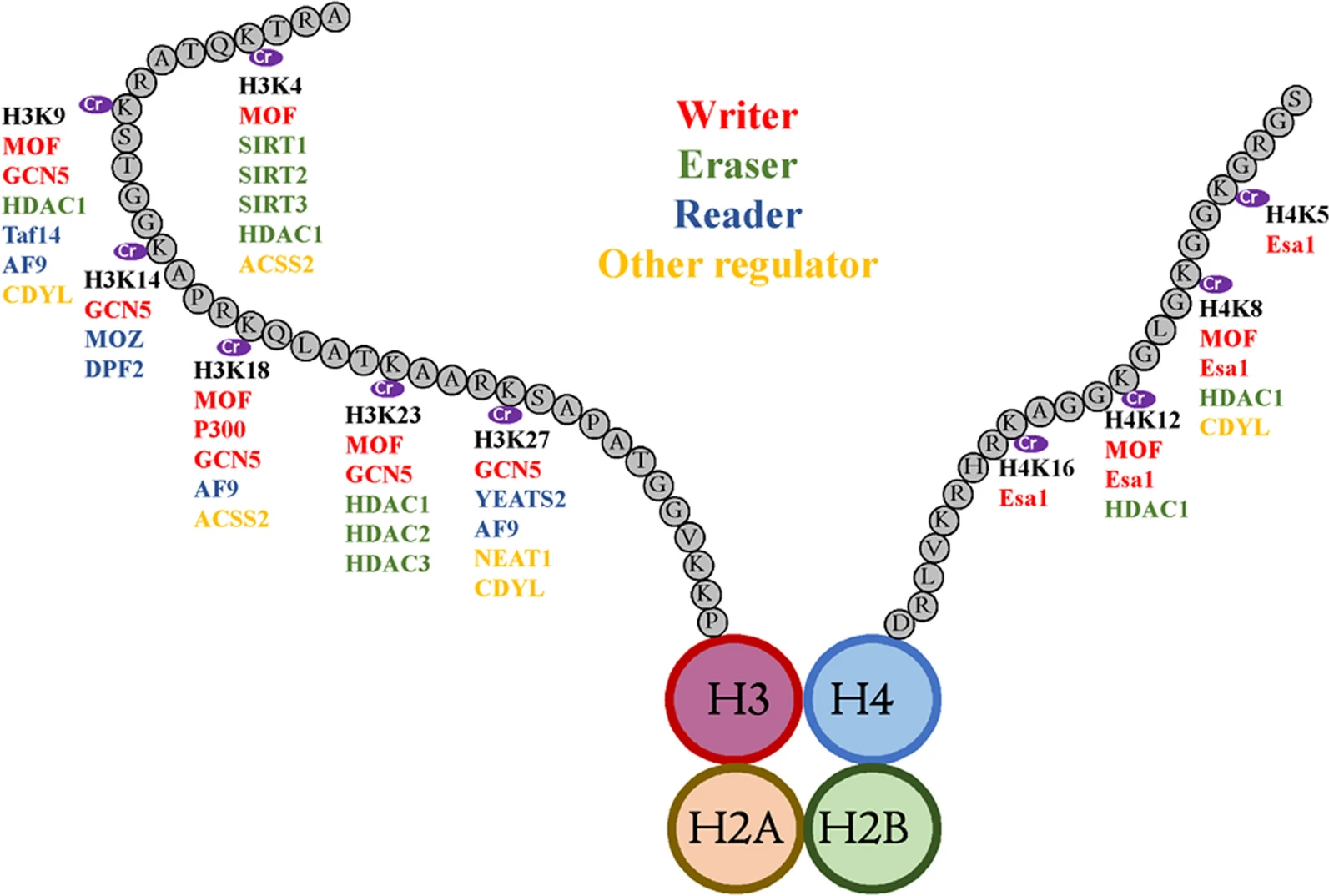
Li, K. et al. Epigenetics & Chromatin, 2021.
Figure 1. Histone Crotonylation and Its Regulating Factors.
Analysis Workflow
1. Histone Extraction and Digestion
Histones are isolated from cell or tissue samples and digested under optimized conditions to generate detectable peptides.
2. Modified Peptide Enrichment
Specific enrichment methods are applied to selectively capture crotonylated peptides, improving detection sensitivity and coverage.
3. LC-MS/MS Detection
Using a high-resolution LC-MS/MS platform, Kcr modification sites are precisely identified and quantitatively analyzed.
4. Data Analysis
Bioinformatics tools are integrated to output results such as modification distribution, abundance changes, and functional annotation, supporting in-depth research.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type and Quantity
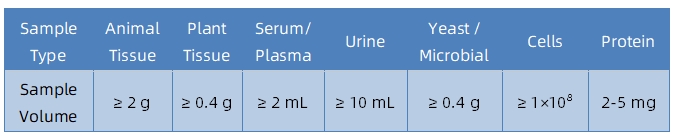
Note: Plasma should be collected using EDTA as an anticoagulant. Standard tissue or cell lysis buffers can be used during protein extraction.
2. Sample Transportation
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Samples are recommended to be stored at -80°C and transported on dry ice to ensure low-temperature conditions throughout the process and prevent modification loss.
Note: For special samples or if a detailed submission plan is required, please contact MtoZ Biolabs technical staff in advance.
Service Advantages
1. High-Resolution Detection
Based on an advanced LC-MS/MS platform, enabling precise identification of low-abundance crotonylation modifications.
2. Efficient Enrichment Strategy
Optimized peptide enrichment methods significantly enhance detection sensitivity and coverage.
3. Strict Quality Control
Standardized procedures and multiple quality control steps ensure stability and reproducibility of results.
4. Customized Experimental Design
Experimental schemes can be flexibly tailored according to research objectives and sample types to meet diverse needs.
Applications
1. Epigenetics Research
Histone crotonylation analysis service can be used to analyze the role of Kcr in chromatin structure maintenance and gene transcription regulation.
2. Gene Expression Regulation Research
By analyzing Kcr modifications under different conditions, it reveals their regulatory effects on gene activation or silencing.
3. Energy Metabolism Research
Histone crotonylation analysis service can be applied to investigate the association between Kcr and metabolic intermediates, exploring its role in metabolic adaptation.
4. Potential Biomarker Discovery
By identifying Kcr modification features under specific conditions, it contributes to the discovery of novel molecular biomarkers.
FAQ
Q1: Which Modification Sites Are Mainly Detected in Histone Crotonylation Analysis?
A1: This service can cover crotonylation modifications on various histone subtypes (such as H3 and H4). Common sites include H3K18cr, H3K27cr, etc., and the detection range can be extended according to research needs.
Q2: What Is the Difference between Crotonylation and Acetylation?
A2: Both crotonylation (Kcr) and acetylation act on lysine residues, but the crotonyl group has a larger structure with an unsaturated bond, exerting stronger regulatory effects on chromatin conformation and gene transcription.
Q3: How Can Histone Crotonylation Analysis Results Be Integrated with Other Omics Data?
A3: They can be integrated with transcriptomics, metabolomics, and other PTM data to construct regulatory networks and analyze the role of Kcr at the systems level.