Histone Ubiquitination Analysis Service
Based on a high-resolution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) platform, MtoZ Biolabs offers the histone ubiquitination analysis service enabling systematic detection and quantitative analysis of ubiquitination modifications on histone lysine residues. This service can accurately identify mono- or polyubiquitination modifications on different histone subtypes and specific sites, and compare their abundance under various experimental conditions. By integrating bioinformatics analysis, the service provides high-quality data including modification site distribution, quantitative results, and functional annotation, offering reliable support for researchers to further explore ubiquitination.
Overview
Histone ubiquitination refers to a reversible post-translational modification in which ubiquitin molecules are covalently attached to histone lysine residues through enzymatic reactions, playing a key role in chromatin remodeling and gene expression regulation. This modification participates in controlling gene transcription, DNA damage repair, and replication by affecting the recruitment of transcriptional complexes, nucleosome stability, and chromatin accessibility. In recent years, histone ubiquitination, as an important layer of epigenetic regulation, has been widely applied in studies of transcriptional regulation mechanisms, chromatin dynamics, as well as systematic investigations of tumorigenesis, development, and immune-related pathways.
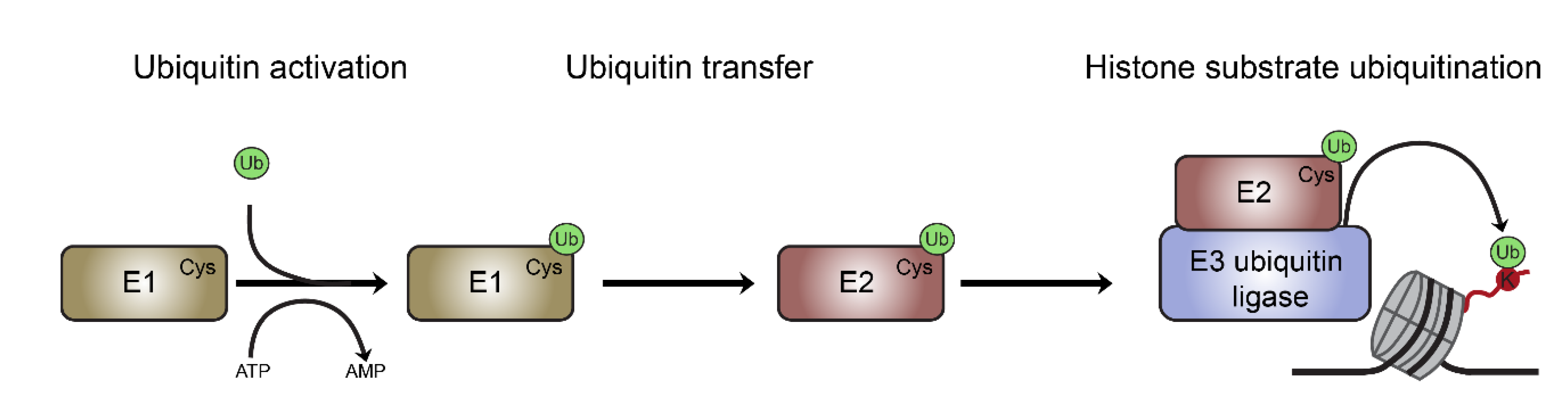
Oss-Ronen, L. et al. Cells, 2022.
Figure 1. The Process of Histone Mono-ubiquitination.
Analysis Workflow
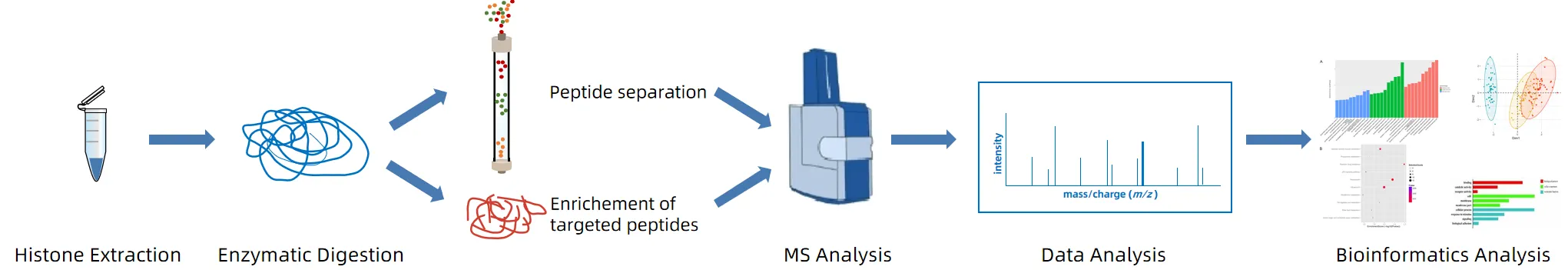
Figure 2. The Workflow of Histone Ubiquitination Analysis.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type and Quantity
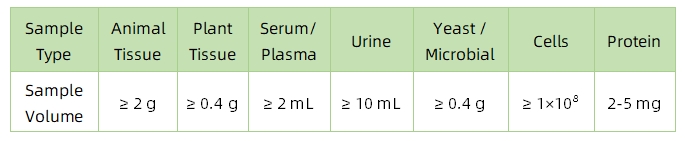
Note: Plasma should be collected using EDTA as an anticoagulant. Standard tissue or cell lysis buffers can be used during protein extraction.
2. Sample Transportation
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Samples are recommended to be stored at -80°C and transported on dry ice to ensure low-temperature conditions throughout the process and prevent modification loss.
Note: For special samples or if a detailed submission plan is required, please contact MtoZ Biolabs technical staff in advance.
Service Advantages
1. High-Resolution Detection
Relying on an advanced LC-MS/MS platform, this service can accurately identify low-abundance ubiquitination modifications and perform quantitative analysis.
2. Specific Enrichment Strategy
Optimized peptide enrichment methods are employed to effectively increase the detection rate and coverage of ubiquitination modifications.
3. Customizable Analysis Workflow
Experimental workflows can be flexibly designed according to sample type and research objectives to meet diverse scientific needs.
4. Strict Quality Control
Standardized procedures are followed from sample preparation to data processing to ensure accuracy and reproducibility of results.
Applications
1. Epigenetic Regulation Research
The histone ubiquitination analysis service can be used to elucidate the role of histone ubiquitination in chromatin structure maintenance and gene transcription regulation.
2. DNA Damage and Repair Studies
By detecting site-specific ubiquitination on histones, researchers can study its regulatory mechanisms in DNA damage sensing and repair processes.
3. Cell Cycle and Differentiation Studies
The service enables analysis of dynamic changes in ubiquitination during cell cycle progression and differentiation.
4. Protein Homeostasis and Signal Transduction Research
Histone ubiquitination analysis service can reveal the critical role of ubiquitination in protein degradation and signaling pathways.
FAQ
Q1: Does the Service Cover Specific Histone Subtypes and Ubiquitination Sites?
A1: Yes. The service can detect ubiquitination sites across multiple histone subtypes (e.g., H2A, H2B, H3, H4), including common sites such as H2AK119ub and H2BK120ub, and the coverage can be expanded based on research needs.
Q2: Can the Service Distinguish between Mono-ubiquitination and Poly-ubiquitination?
A2: Yes. Using specific enrichment strategies combined with high-resolution LC-MS/MS, the service can accurately identify mono-ubiquitination, chain-type poly-ubiquitination, and different ubiquitin chain types.