Applications
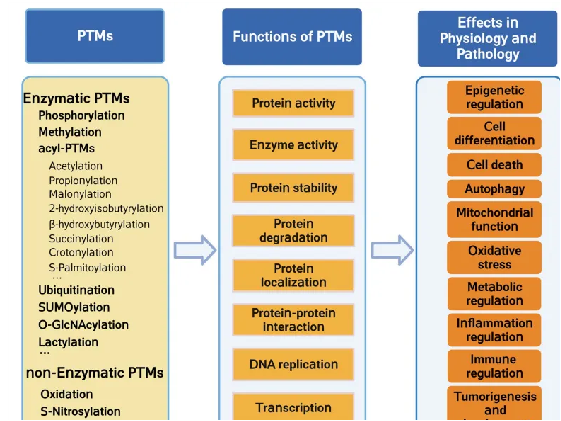
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) are fundamental mechanisms that regulate protein function and cellular activities. By dynamically modulating protein activity, localization, interactions, and stability, PTMs play pivotal roles in biological processes such as signal transduction, metabolic regulation, gene expression, and stress responses. Under normal conditions, PTMs ensure the orderly maintenance of cellular homeostasis and physiological functions; however, once dysregulated, they often lead to the onset and progression of major diseases.
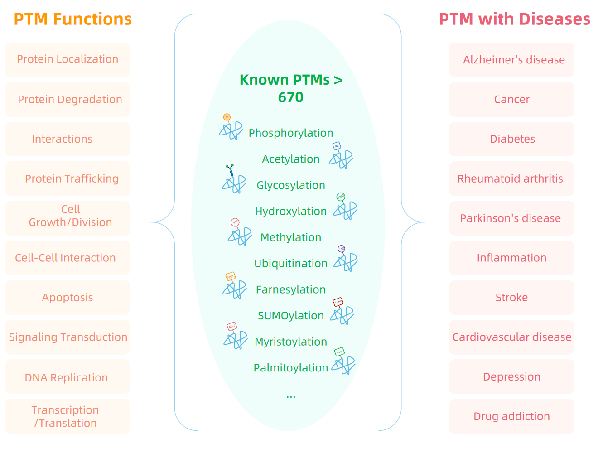
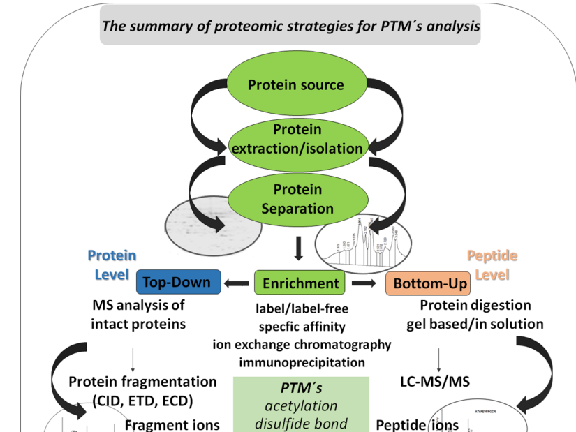
In recent years, with the rapid advancement of mass spectrometry-based proteomics, researchers have been able to systematically characterize diverse types of PTMs, thereby providing powerful tools for drug target discovery, mechanism-of-action studies, and biomarker identification. This progress has not only advanced fundamental life science research but also opened new avenues for applications in biopharmaceutical development, disease research, as well as agriculture and microbiology.
|
PTMs can dynamically alter protein activity, localization, interactions, and stability, allowing them to play central roles in biological processes such as signal transduction, metabolic regulation, gene expression, and stress responses. |
PTMs are essential for maintaining normal physiological functions, and once dysregulated, they often trigger diseases. |
With the rapid advancement of mass spectrometry-based proteomics, it is now possible to systematically analyze PTMs, providing powerful tools for drug target discovery, mechanism-of-action studies, and biomarker identification. |
|
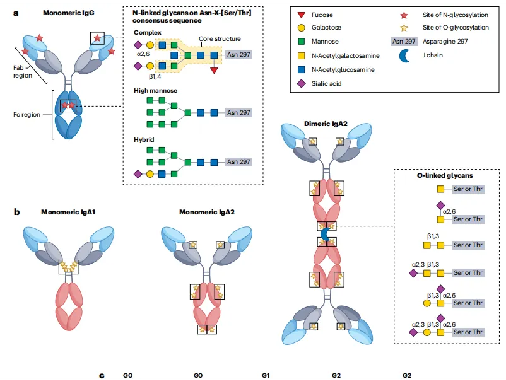
PTMs can significantly influence the stability, conformation, solubility, and half-life of protein drugs, as well as regulate their interactions with receptors or ligands, thereby determining therapeutic activity and efficacy. |
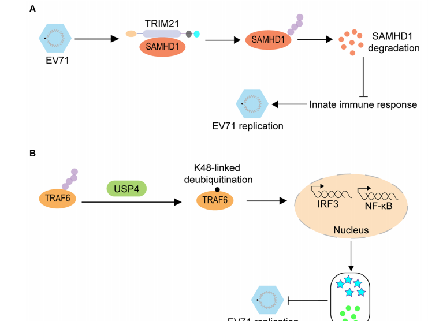
As research progresses, the types of PTMs identified in microbes continue to grow, and these modifications have been shown to regulate metabolism, signal transduction, environmental adaptation, and virulence expression. |
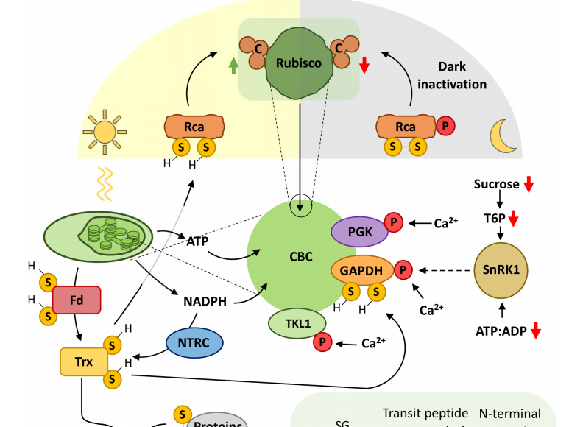
Proteins undergo diverse post-translational modifications (PTMs), including phosphorylation, glycosylation, acetylation, methylation, ubiquitination, SUMOylation, and redox modifications. These chemical alterations greatly expand protein functional diversity, allowing plants to rapidly and dynamically adjust molecular networks during development and under environmental stress. |
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (MS) Services Provider, provides advanced proteomics,metabolomics, and biopharmaceutical analysis services to researchers in biochemistry, biotechnology, and biopharmaceutical fields. Our ultimate aim is to provide more rapid, high-throughput, and cost-effective analysis, with exceptional data quality and minimal sample consumption. To gain deeper insights into the biological significance of post-translational modifications and translate scientific discoveries into practical applications, advanced analytical strategies are essential. Contact us to explore how our customized solutions can support your next research project.